RNase I degrades single-stranded RNA to nucleoside 3'-monophosphates via 2', 3' cyclic monophosphate intermediates by cleaving every phosphodiester bond. RNase I completely degrades RNA, unlike RNase A that cleaves only after cytosine and uridine. In addition, the enzyme is completely inactivated by heating at 70°C for 20 minutes, eliminating the requirement to remove the enzyme prior to many subsequent procedures.
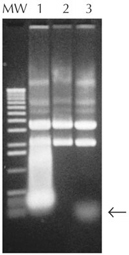 |
| Figure 1. Removal of RNA from plasmid DNA preparations. Plasmid DNA was prepared from 1.5 ml of an overnight culture, suspended in 50 µl TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 1 mM EDTA), and treated with RNase A, RNase I, or no enzyme. Five µl of each reaction were resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide. Lane 1, no RNase; Lane 2, 1.5 U of RNase I; Lane 3, 20 µg/ml RNase A; MW, 1-kb ladder. Arrow denotes small undigested RNA. |
Unit Definition
One unit degrades 100ng of E. coli ribosomal RNA per second into acid-soluble nucleotides at 37°C in 10mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 100mM NaCl, and 1mM EDTA.
Dilution and Storage Buffers
50mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 100mM NaCl, 0.1mM EDTA in 50% glycerol.
Quality Control
RNase I is free of detectable DNA exo- and endonuclease activities.
If you cannot find the answer to your problem then please contact us or telephone +44 (0)1954 210 200