Min-Immune™ Gold dsRNA Removal Kit

Product Description
The Min-Immune™ Gold dsRNA Removal Kit provides a novel enzymatic
solution for the removal of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) contamination
present in RNA samples produced by in vitro transcription (IVT). Each 25-reaction kit will treat 1,500 μg of IVT RNA or mRNA.
The removal of dsRNA from mRNA preparations has been shown to be
essential for reducing the innate immunogenic response to the mRNA in
cells.1-4 Alternative dsRNA removal methods, such as reverse-phase HPLC,5 hydroxyapatite chromatography6 and cellulose chromatography,7
are associated with high capital costs as well as reduced final product
yields. The Min-Immune™ Gold dsRNA Removal Kit provides an easy to use,
scalable method for removing the dsRNA content of IVT or mRNA preps
without a reduction of the single-stranded RNA yield.
- Easy to use, scalable enzymatic method for removing double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) from RNA samples.
- Remove dsRNA without the need for chromatographic methods like HPLC.
- No reduction in single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) yields.
- Reduces the innate immunogenic response to mRNA in cells.
Uses and Label Licenses for Specific Products: See the Licensing tab for more information.
Product Performance
dsRNA reduction
A Min-Immune™ Gold dsRNA Removal Kit treated 1.4 kb
pseudouridine-containing RNA sample was compared to an untreated sample
(Figure 1, right panel) and dsRNA Standards (Figure 1, left panel).
Triplicates of each sample and standard were immobilized on a charged
nitrocellulose membrane, then immunoblotted with a primary
dsRNA-specific antibody and a secondary antibody conjugated to
horseradish peroxidase (HRP). Signal was detected using enhanced
chemiluminescence on a Syngene® G:Box. A regression equation was
generated using the dsRNA standard curve on the left and is used to
calculate the percent dsRNA present in both the treated and untreated
samples seen on the right side of the blot. Results show a reduction of
dsRNA content in the treated sample replicates to levels below the limit
of detection (0.005%) of this assay after treatment with the
Min-Immune™ Gold dsRNA Removal Kit.
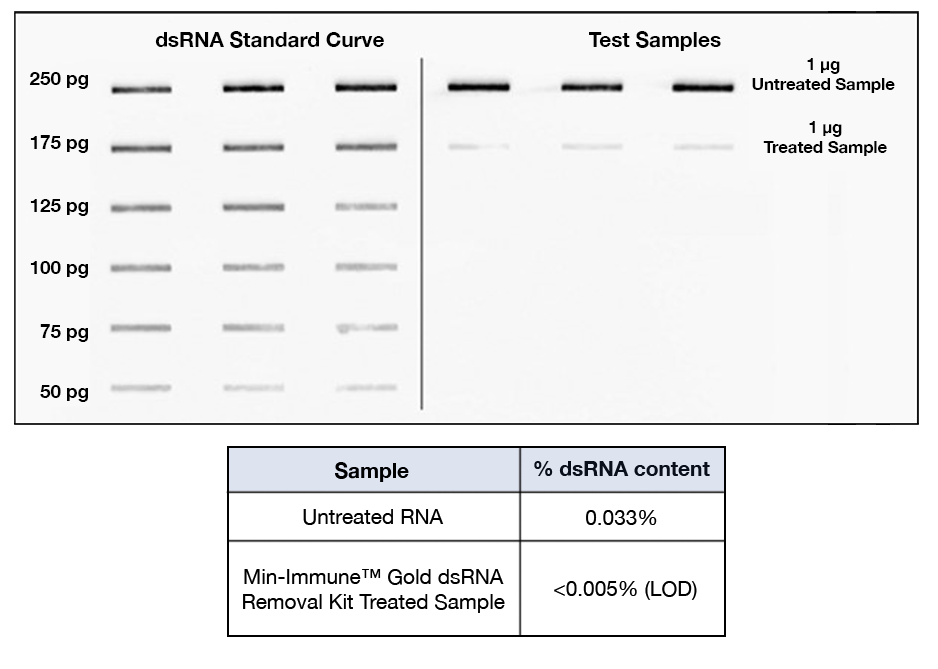
Figure 2. dsRNA
immuno-dot blot assayed with dsRNA-specific J2 antibody detection using
horseradish peroxidase and chemiluminescent detection. 1 µg of Untreated
or Treated mRNA was blotted for each experimental sample.
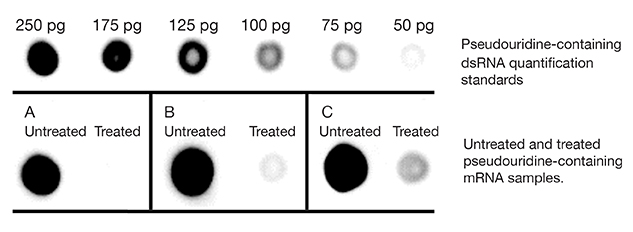
Panel A: Example result of an mRNA prep where the dsRNA content is
totally removed by treatment. This mRNA can be used for downstream
applications.
Panel B: Example result of an mRNA prep where the mRNA contains an
inherent dsRNA region which is not recognized by Min-Immune™ Gold RNase
III but is recognized by the J2 antibody. This mRNA can be used in
downstream applications.
Panel C: Example result of an mRNA prep where the dsRNA content is
not totally removed by treatment. This mRNA would require retreatment
prior to many downstream applications.
Important Store at -20°C in a freezer without a defrost cycle. Do not store at –70°C.
|
Min-Immune™ Gold dsRNA Removal Kit Contents (25 reactions) |
|
Kit Component |
Reagent Volume |
Min-Immune™ Gold RNase III (20X)
in 50% glycerol, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, 1 mM
dithiothreitol (DTT), 0.1 mM EDTA and 0.1% Triton® X-100.
|
150 μl |
|
Min-Immune™ Gold 10X RNase III Treatment Buffer |
300 μl |
ScriptGuard™ RNase Inhibitor, 40 U/μl
in 50% glycerol, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM DTT, 0.1 mM EDTA and 0.1% Triton X-100. |
75 μl |
|
5 M Ammonium Acetate |
2 x 1.6 ml |
|
RNase-Free Water |
2 x 1.7 ml |
Materials Required, but not Supplied
- mRNA or IVT RNA for treatment.
- 70% ethanol
Optional Materials
dsRNA-specific detection system including:
- dsRNA-specific antibody (e.g., J2 antibody [Absolute Biotech-Exalpha])
- Dot/slot blotting system for use with the antibody
- An image analyzer for blot visualization and/or quantification
- dsRNA standards
References:
- Karikó, K. et al., (2011) Nucleic Acids Res. 39, e142.
- Schlee, M., Hartmann, G., (2016) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 566.
- Pardi, N. et al., (2018) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17, 261.
- Mu, X., Hur, S., (2021) Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 4012.
- Weissman, D. et al., (2013) Methods Mol. Biol. 969, 43.
- Kalmakoff J., Payne C.C., (1973) Anal. Biochem. 55, 26.
- Baiersdörfer M. (2019) Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 15, 26.
If you cannot find the answer to your problem then please contact us or telephone +44 (0)1954 210 200